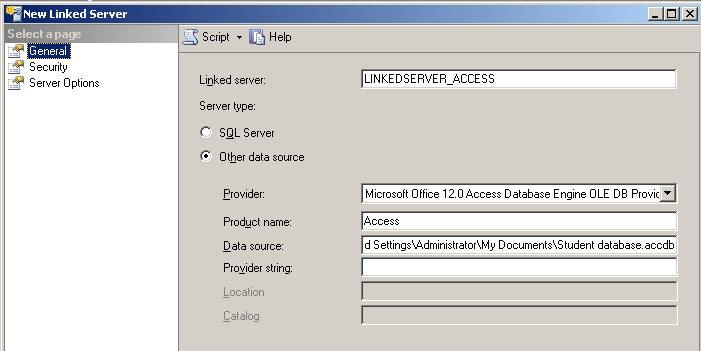
This article will guide through the steps to install .NET Framework 3.5 on a Windows Server 2008 R2.
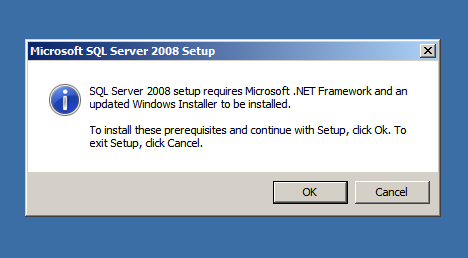
I recently installed and started working on a Windows Server 2008 R2 Enterprise. I started installing SQL Server and I knew SQL Server 2008 requires the Microsoft .NET Framework 3.5 to be installed on the machine. The installation wizard displayed the following message box (picture below), which is common. (as I had previously installed SQL Server 2008).
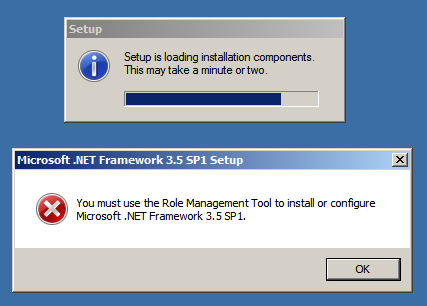
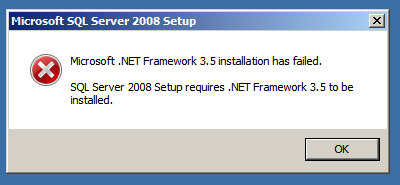
I clicked OK button and the setup started loading the required components and immediately displayed the error message (picture below), asking to install .NET Framework from Role Management Tool.
To install roles on a Windows Server the roles have to be added in the Server Manager. So I opened the Roles node from the tree structure in the Server Manager and what you see below is what it looks like (only required portion of the screen is shown to make the images smaller and tidy). On the right side, Add Roles is available and we need to select / click that.
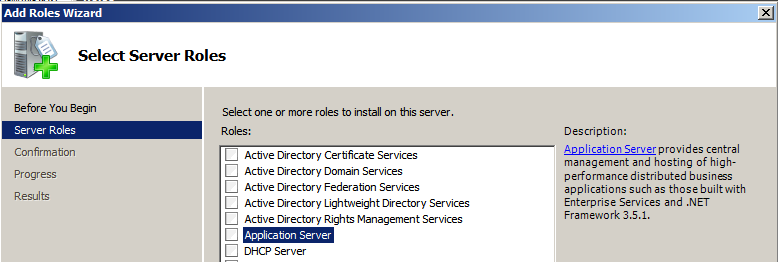
Upon selecting Add Roles, the Add Roles Wizard is displayed as shown below. I selected Application Server and on selecting it, there is a description available on the right side, what that role is going to provide or include.
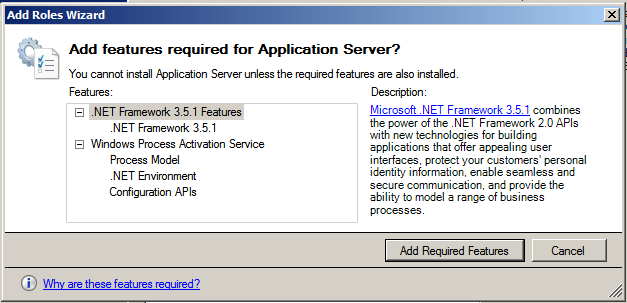
The following information message box is displayed informing that to install an Application Server, there are certain other required features we need to include. All we need to do is to click the Add required features button in the message box.
It would then display the dialog box giving a short information of what an Application Server does. Click Next to continue.
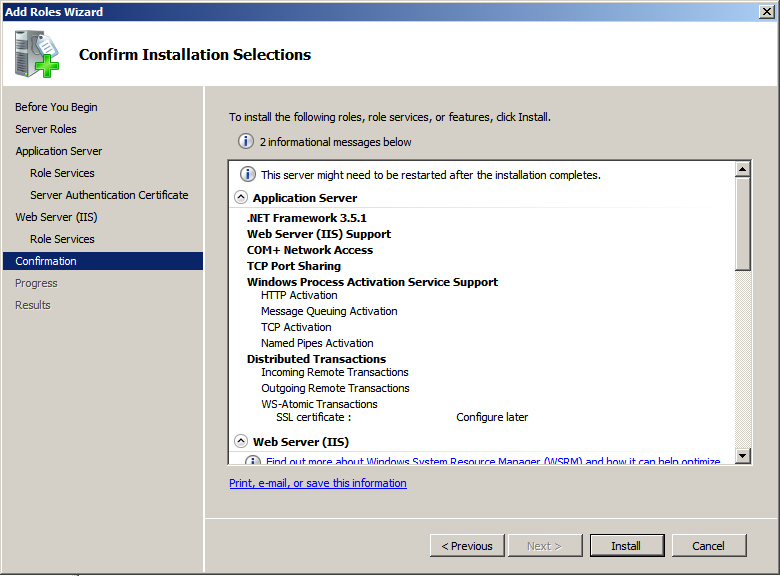
I choose some additional roles apart from Application Server role, and the dialog box below is a confirmation of all the selections, click install to start the installation process.
The Installation begins. (Picture Below)
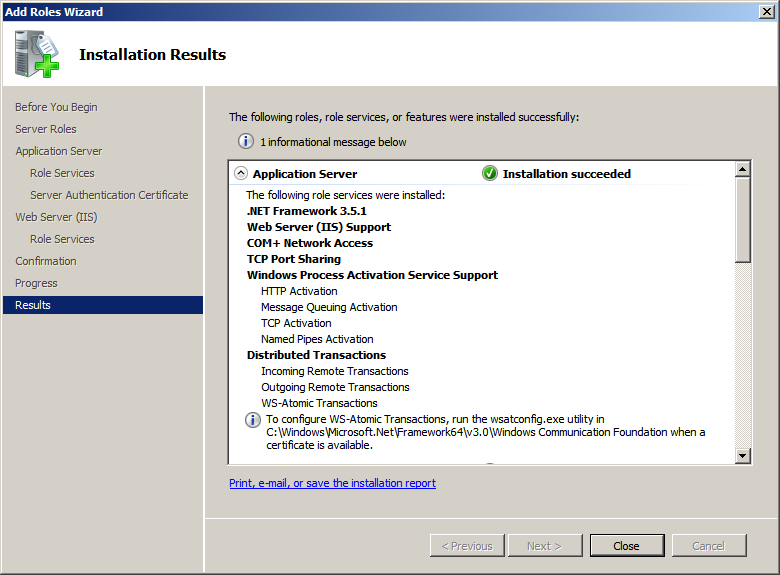
The installation is successful and the picture below is the dialog box confirming the success of the installation of the roles that we have chosen.
With that, the prerequisite for installing a SQL Server 2008 Instance is met, and we can continue installing SQL Server 2008.
Do you like this site? Like our FB page @ Facebook.com\LearnSQLWithBru that let’s you know when there is a new blog post.
–Bru Medishetty