CHAPTER 1 – Preparing your system and Installing SQL Server for the first time
What you need to start learning SQL Server?
First thing you would need is a decent laptop (or a desktop), I prefer laptops as they can be taken with you wherever you go. A laptop bought in recent 2-3 years should be good. Once you have that, you need software to install SQL Server. SQL Server Developer Edition is your best bet to start working on SQL Server, and you can buy it directly from Microsoft Store from this link. (Tip: Use the search box for finding the Developer Edition, it is not listed). It costs you approx 50 bucks to buy your copy of SQL Server and you do not have to worry about any missing features. We will learn more on Developer Edition and other Editions later on in the course. Another choice is to download an evaluation edition, which expires after 180 days of installation. You can download SQL Server 2008 R2 Evaluation Edition from this link.
The following is added on Nov 21st 2011
How to setup your first SQL Server?
By the time your software is delivered or downloaded, you will have to figure out what is the Operating System (OS) on which you are going to install SQL Server. Once you figure out that, go to Books Online (see links below) for minimum software requirements to install the SQL Server Version and Edition you are planning to install.
Note: SQL Server 2005, 2008, 2008 R2 and 2012 are Versions, whereas Editions are Express, Developer, Enterprise Evaluation, Standard and Enterprise…. (more details are explained in a separate blog post What are Versions and Editions in SQL Server)
The following are Books Online links to know about the Minimum Hardware and Software requirements for various SQL Server Versions.
For SQL Server 2012 For SQL Server 2008 R2 For SQL Server 2008 For SQL Server 2005
A little reading and planning ahead will save you lot of frustration while you install SQL server. I recommend you spare a little time and read the 2 blogs Rules to follow while naming a SQL Server Instance and Examples for naming SQL Server Instances. If you are planning to install a named instance, (or at least 2 Instances on a single machine) those blogs will help you in naming your SQL Instance.
Installing SQL Server for the first time
Before beginning installation, keep your system ready by installing the latest Service Packs for your OS and other prerequisites (such as .NET). Read the steps to Install .NET 3.5 Framework in Windows Server 2008 R2 that I wrote in December 2009. You might also want to restart you machine to save some time (If there is a pending system reboot, SQL Server Installation will ask you to reboot and start the installation steps.)
Once you are ready to install, look at this blog Installing SQL Server 2008 R2 Explained for a step by step Installation of SQL Server 2008 R2. Additionally if you are looking for Installing SQL Server 2012 read this blog Installation of SQL Server SQL Server 2012.
I hope you have enough information on how to set yourself a SQL Server machine that will open doors for you to explore and learn SQL Server stuff. In case you have to uninstall the SQL Server 2012 Installation, you can do so, just follow the comments of the blog Installation of SQL Server 2012.
============================================================== The following is added on Dec 31st 2011
CHAPTER 2 – Introduction to various SQL Server tools
What tools are used while working with SQL Server?
In this chapter our main goal is to get introduced to all tools used while working with SQL Server. Tools provided available out of the box, when SQL Server is installed along with some Windows tools. This chapter does not include any 3rd party tools available for SQL Server…
Those tools are SQL Server Management Studio, SQL Server Configuration Manager, SQL Server Profiler, Database Engine Tuning Advisor, Business Intelligence Development Studio and System or Performance Monitor.
The following is added on Jan 5th 2012
SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS)
SSMS is the most frequently used tool in SQL Server. SSMS has been introduced in SQL Server 2005, replacing and Enterprise Manager in SQL Server 2000. SSMS provides the interface to connect to SQL Servers and work with those Instances. The reason why SSMS is so important tool in SQL Server is, almost 90 % of day-to-day activity can be performed from SSMS. There may be hundreds of tasks that can be performed in SSMS, out of which I shall list a few, to show what tasks can be performed from SSMS.
The following are some of the tasks you can perform in SSMS.
- Start / Stop SQL Server Instance.
- Create / Drop Databases.
- Perform Backup / Restoration of Databases.
- Create, Modify, Delete logins to SQL Server.
- Assign permissions to the users.
- Create SQL Server Agent Jobs.
- Monitor the activity of the SPIDs connected to SQL Instance.
- Write SQL Server code.
- Run commands / scripts to troubleshoot problems related to deadlocks or get diagnostic information.
- Create / Modify and Delete Database objects such as Tables, Views, Stored Procedures, Functions, Triggers etc.
- Perform all tasks related to Replication, Database Mirroring and Log Shipping, some of the tasks are Initially setting up the HA, monitor the functioning, troubleshoot issues based on day to problems.
- Performance tune SQL Server Queries.
As mentioned earlier, there are many other tasks that can be carried out in SSMS, the above is just a little portion on those tasks. You will learn more as you go deeper into those topics…
The following is added on Jan 8th 2012
SQL Server Configuration Manager
SQL Server Configuration Manager is a tool that is useful in making server level configuration settings. You can enable / disable protocols that are used by the SQL Server for connecting to local and remote clients. This tool is one of the ways you can start / stop or pause SQL Server Database Engine. One of the benefits of Configuration Manager is, you can take a look at the status of all of the SQL Server Services instances on the machine. The below pic is taken from one of my previous bogs which shows the list of SQL Server services on a server.
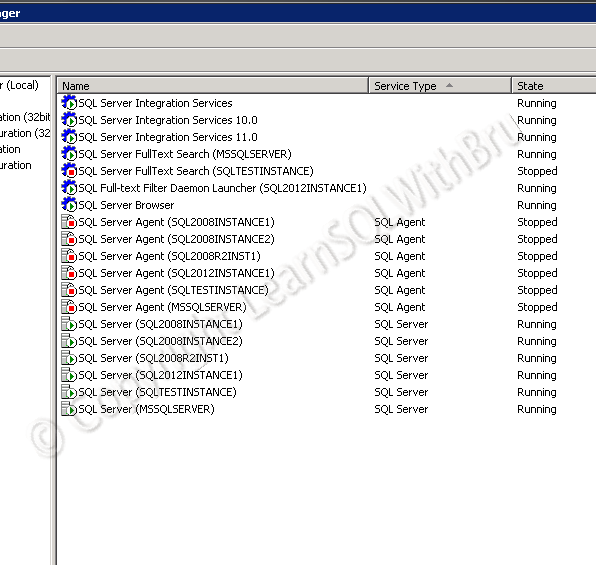
The following are some of the tasks you can perform using Configuration Manager.
- Start / Stop or Pause a SQL Server service.
- Make changes to Start-up Parameters for a SQL Server Database Engine.
- Configure the services (SQL) to start automatically or disable or set to a manual start mode.
- Enable / disable the protocols which the SQL Server uses to connect to client machines.
- Change the TCP/IP Port number on which SQL Server accepts connections.
- Add or modify to the account under which SQL Server runs.
And few more tasks. All in all Configuration Manager is generally used by Database Administrators to configure stuff related to the SQL Server Services, SQL Developers do not have much to do in this tool.
The following is added on Feb 22nd 2012
Business Intelligence Development Studio
The next tool we would learn in this chapter is Business Intelligence Development Studio, also called as BIDS. This tool is primarily used by Developers while working with the BI part of SQL Server (SSIS, SSAS and SSRS). Working with BIDS is very easy if a user has prior experience working with Visual Studio. If you haven’t worked with Visual Studio, then you don’t have to worry too much, as getting to know how to work in BIDS is easy to learn and also is fun. In fact BIDS is actually a little wrapper on top of Visual Studio.
Some of the tasks which can be carried out from BIDS are.. ..
- Create various kinds of reports, some of them are tabular, matrix, drill through, charts and drill down reports.
- Preview the reports while designing and testing.
- Deploy the finished reports.
- Create and test run SSIS packages (and a ton of individual tasks that can be incorporated in an SSIS package).
- Build SSIS packages in order to deploy them.
- Build Analyisis Services Cubes, dimensions and preview the cubes.
As you can see, the tasks that can be done from BIDS are more or less the job responsibilities of a SQL Server / BI Developer, indicating that this tool is more utilized by developers than admins.
The following is added on Mar 2nd 2012
SQL Server Profiler
SQL Server Profiler is another tool in SQL Server that is commonly used in a SQL Server environment. This tool is a much needed tool for a SQL Server DBA to investigate a variety of issues. Though this tool is listed under performance tools along with Database Engine Tuning Advisor, I personally think this tool is useful in situations other than just a performance tuning scenario. When I say that, I often find Profiler to be very useful in investigating issues such as login failures, like what application is trying to access the SQL Server using this login. SQL Server error log only gives information on the IP address from where the login is failing but not more than that. Using Profiler is that case gives me more information on the problem at hand. There are several other useful scenarios in which Profiler is very useful..
The following is added on Jun 15th 2012
CHAPTER 3 – SQL Server Post Installation
What’s next after Installing SQL Server?
You are done installing SQL Server (chapter 1) and you have gone through the various tools available in SQL Server (chapter 2), in this chapter we will look at what’s next…
Connecting to SQL Server through SSMS
If this is the first time you are working with SQL Server, in order to start using SQL Server and learn it, you have to connect to SQL Server. One of the easiest ways to connect and working with SQL Server is through SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS). In this blog, I explained the different ways of connecting to a SQL Server based on the Instance (default or Named Instance).. Read the blog Connecting to Named and Default Instance in SQL Server.
The following is added on Jun 27th 2012
Once you are able to connect to a SQL Server, you should get yourself acquainted to the SSMS tool and navigate around. As mentioned in previous chapter (read the SSMS section in chapter 2), there are host of tasks, in fact most of the work on a SQL Server is carried out from SSMS.
To be continued…..
Please feel free to send your feedback and suggestions on what topics you would like to see here and I shall try to incorporate them when possible.
Do you like this site? Like our FB page @ Facebook.com\LearnSQLWithBru to know when there is new content.
–Bru Medishetty

where is the third chapter sir
Asif, the 3rd chapter is not yet published.. Sorry for any confusion caused..
The reason I made it chapters1-3 is to have multiple chapters on a single web page, else it would be a long list of chapters, as I keep adding them.. Hopefully it should be out in 2-3 weeks, sometime in Feb 2012..
Thanks BRU Brother
Thanks…
What about installing SQL Server 2008 or 2012 Developer on a laptop – what are the ‘tricks’ to that – I have a technet subscription and tried to install 2008 R2 on my laptop and have had difficulties with it…
Can you let me know what is the issues you ran into on your laptop.. ?
Excellent Bru!
I am Jr. SQL DBA and preparing for 70-432 Exam.
If possible please suggest some guidline for certification seekers!
Kind Regard,
Ashvini