In this blog, let’s take a look at different ways we can check the date and time SQL Server was started last time. There are multiple ways to do it and each of them has its pros and cons.
Using TempDB
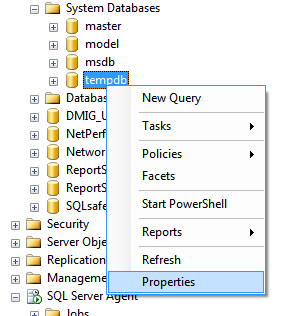
The first method we shall look is to see when was the TempDB created. If you recollect, one of the first things you have learnt about TempDB is it a database used to store objects temporarily and is refreshed/ recreated every time SQL Server is started. Here we would use the creation time of TempDB to determine when was the SQL Server started last time. To do this, open SQL Server Management Studio, go to object explorer, expand databases node/folder. Expand System databases and right-click on Tempdb as shown below and choose properties.
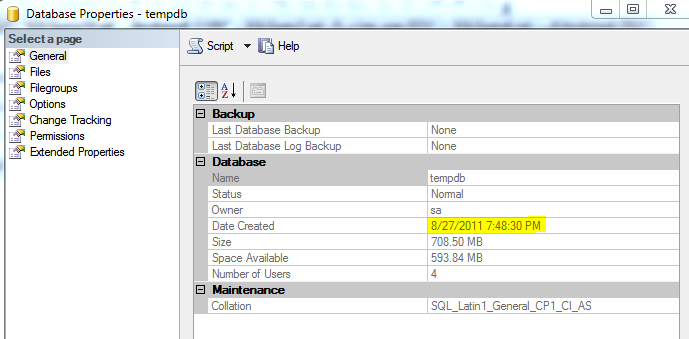
Database properties window of Tempdb is displayed. In the very first screen when the General page is selected you can notice the Date Created column (highlighted below)…
This way of finding information from Tempdb creation is the easiest way I feel. This step is
SQL Server Error Log
Another way of finding the same information is from the SQL Server Error Logs. This is also one of the easier ways of finding the SQL Server start time, but can be tricky sometimes, which I shall explain in a while..
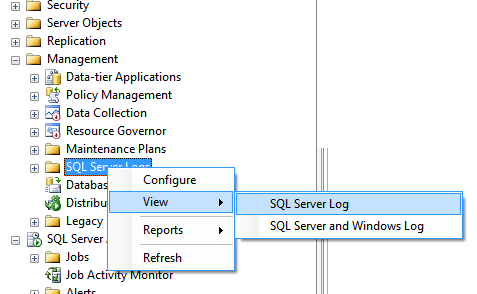
First let’s take a look at the steps to perform this task. In object explorer, expand the Management node and find SQL Server Logs. Right click on SQL Server Logs and go to View –> SQL Server Log (as shown below). These SQL Server Logs contain very important information regarding that SQL Server. Every time SQL Server is started, entries are written in the SQL Server Log.
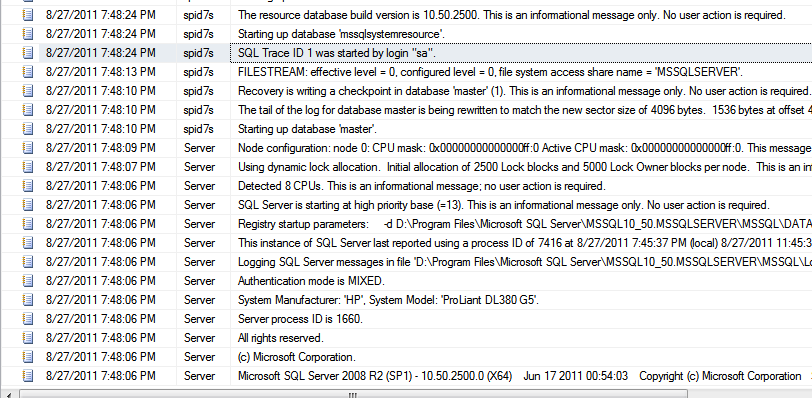
When the entries in Error Log are displayed, you can scroll down to the row which contains the SQL Startup information. In the picture below, look at the entry at 8/27/2011 7:48:06 PM.
It looks like you could find the startup information in SQL Error Log easily, but in some cases it might not be that way. Every time a database backup is performed, there is an entry in the SQL Server Error Log which on an SQL Instance with multiple databases will result in a large number of entries and it would make it difficult to find this information easily. Also, in some cases the Error Log would be regularly recycled in order to ensure that it is easier to read the Error Log and once the maximum number of Error Logs are reached, SQL Server disposes the oldest Error Log when it has to create a new one.
There are other ways to find the SQL Server startup time, which we shall look in my next blog.
Part 2 of this blog can be found here How to find the last time SQL Server was started? Part ll
Do you like this site? Like our FB page @ Facebook.com\LearnSQLWithBru so that, you know when there is a new blog post.