This blog will provide a step by step details of installing SQL Server 2008 Service Pack 3 on more than 1 Instance at the same time. Before going ahead and installing Service Pack, I would recommend you read one of my earlier blogs Best Practices for applying SQL Server Service Packs.
In one of my previous blogs (read it here), you can find where to download the Service Pack, what are the enhancements to SQL Server and few useful links that would assist you in preparation to applying Service Pack 3 for SQL Server 2008.
Once you have downloaded the Service Pack 3, copy the .exe file to a local drive and right click on the file and choose Open from the popup menu to begin the installation. (You can alternately double click the file to begin the installation).
The exe file take a min or two (depending on your system) and extracts to a temporary location, once the extraction is completed, the below Welcome screen is displayed and the installer performs few checks and displays the below screen. If there are any failures, ensure that the necessary steps are performed. Click Next to continue installation.
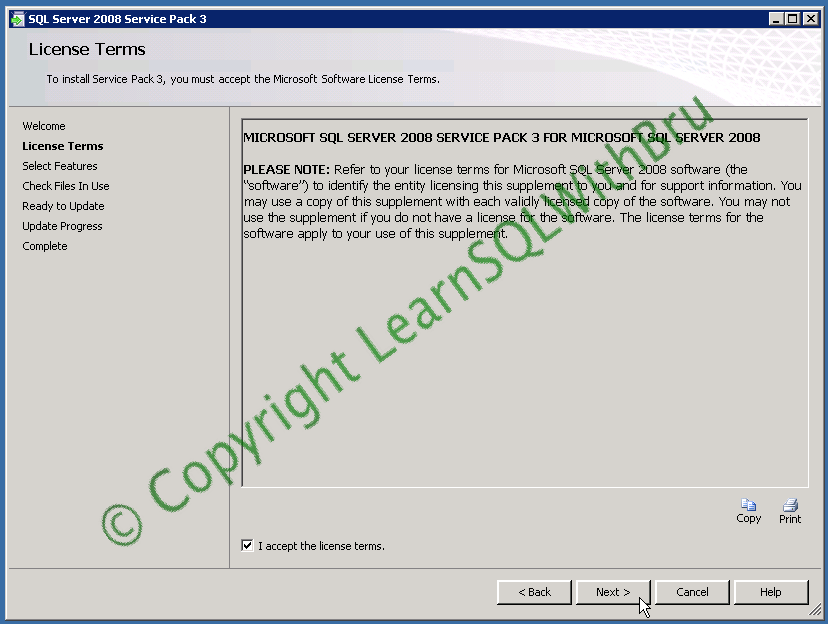
Accept the license terms by selecting the check box and click Next to proceed.
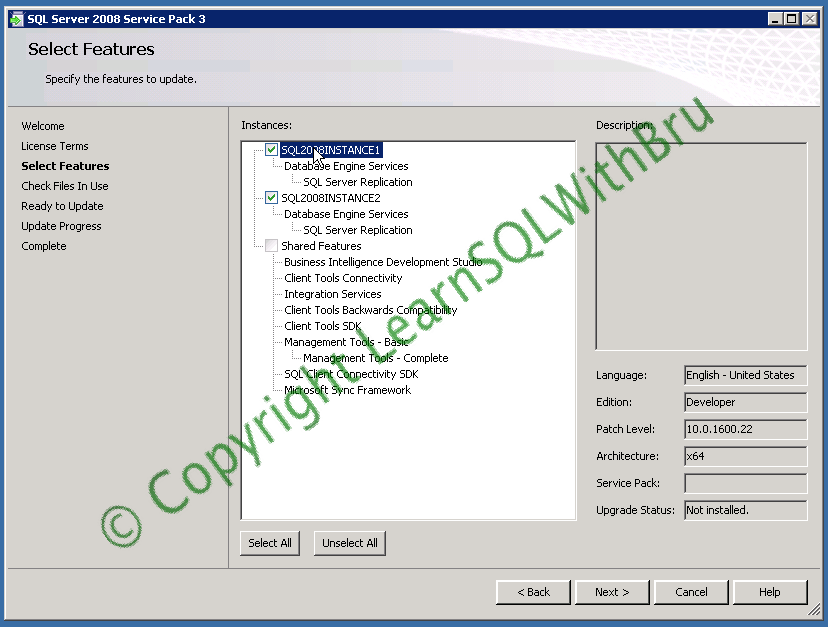
The next step is features selection, where you have to choose the components to which you would like to apply the Service Pack 3. In this blog we are going to apply SP3 for 2 instances at the same time. If you have more than 1 SQL 2008 Instance on the machine, you can choose which instance(s) to apply Service Pack. You can select the check boxes beside each of the Instances or if you wish to Install for all Instances / features click Select All button in the bottom left.
You can click on the Instance to see the current details of that Instance / feature. In the picture below, I clicked on the SQL2008INSTANCE1 and the Edition, Patch Level and other details are displayed..
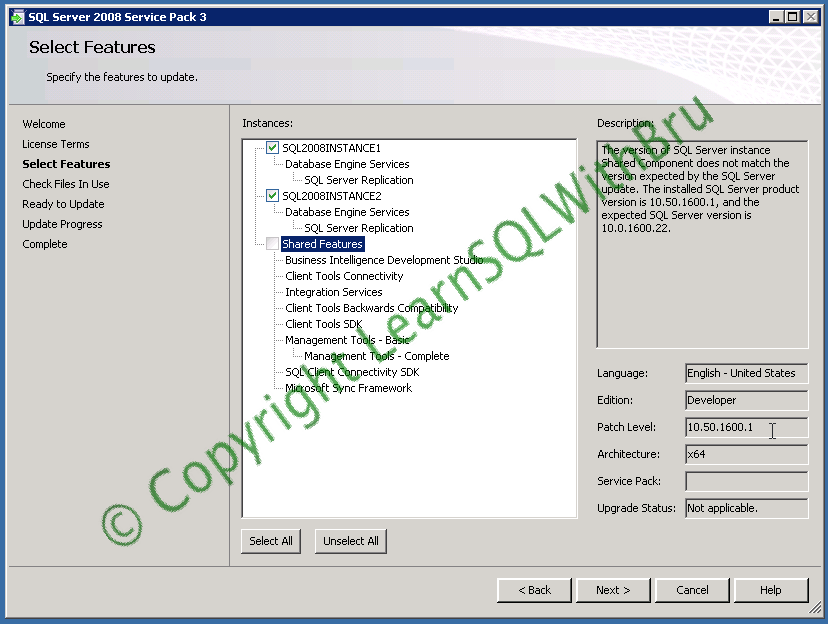
The machine on which we are working in this blog, has a SQL Server 2008 R2 instance installed. Due to this, the Shared Features of SQL Server 2008 are all upgraded when the R2 instance is installed, because of this, we cannot select the Shared Features and apply SP3 to shared features. (see pic below and the description, in the right)
Click Next after you are done selecting the features to be applied with SP3.
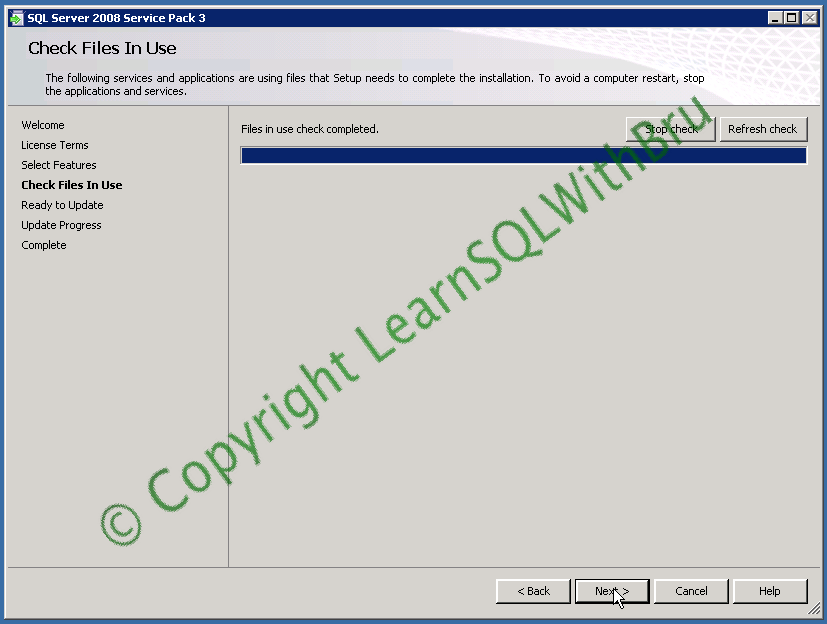
The next step check for the files / services that are being used currently and lists if there are any files that needs to be stopped in order to avoid a restart.
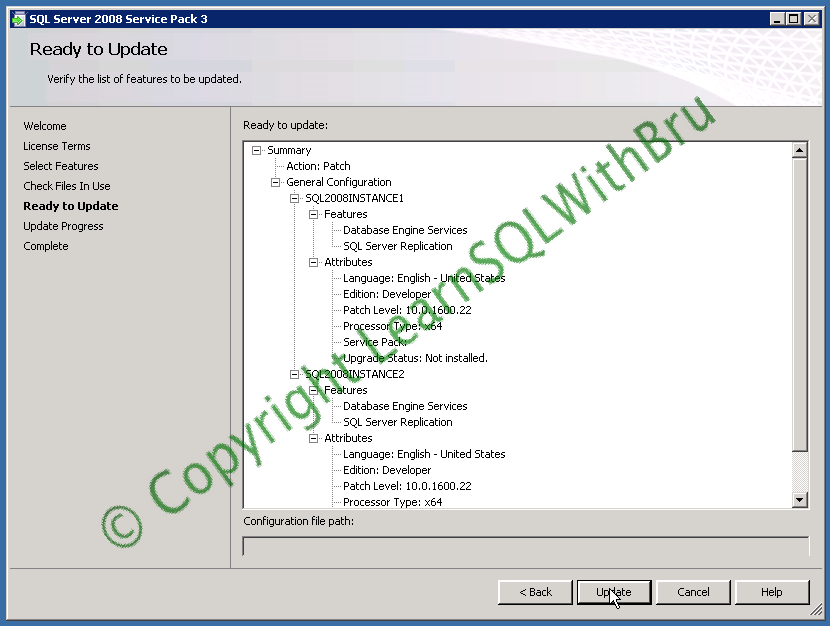
Click Next to proceed. Then the below screen is displayed which shows a summary of features that are going to be updated to Service Pack 3. Click Update to start the SP 3 installation.
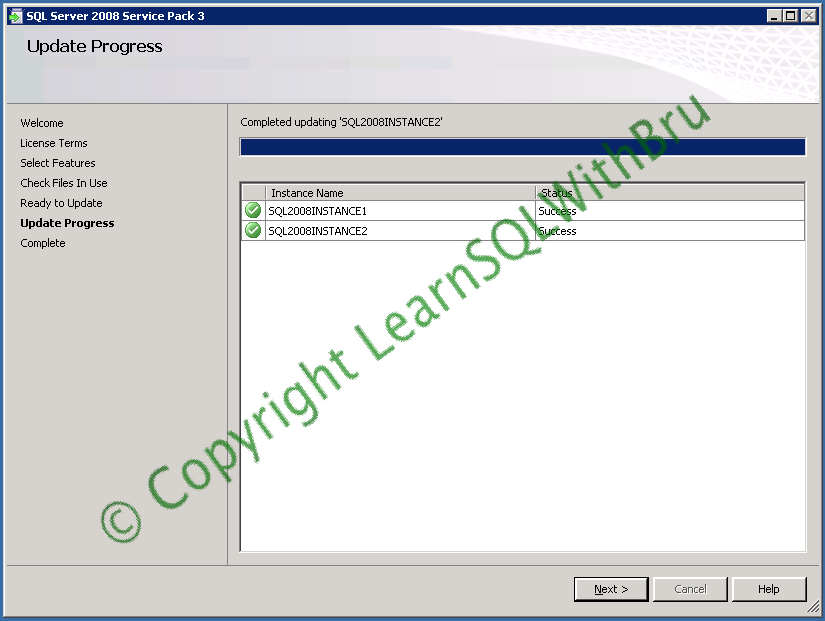
Once the Installation is done, the installation progress is displayed as below.
Click Next to proceed.
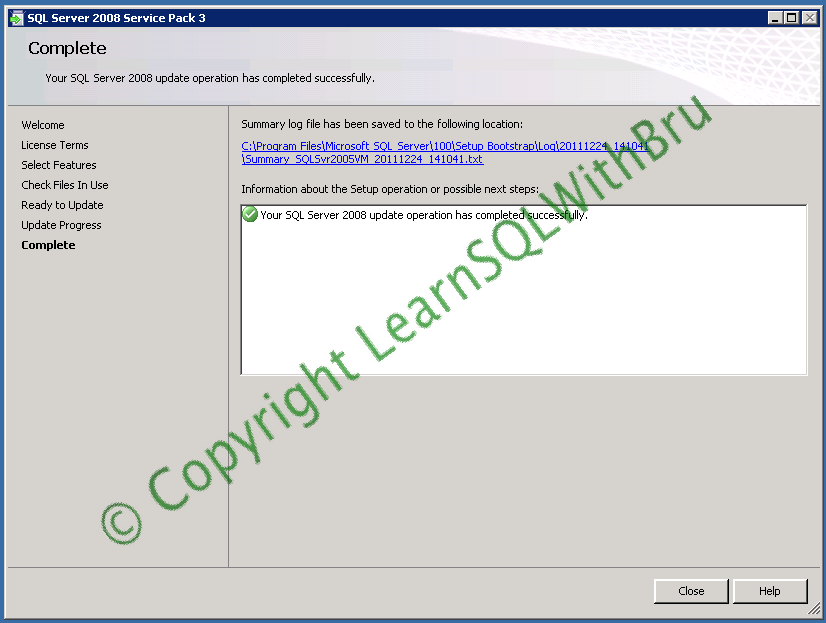
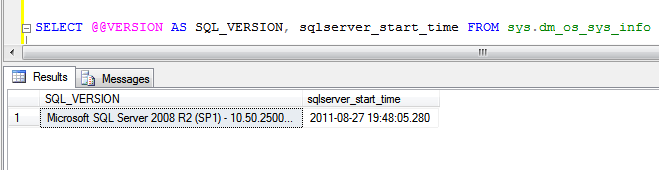
Click Close to close the Service Pack Installer. Restart the machine if possible, else the SQL Instance(s) that have been updated with the Service Pack 3. Once the Instance is restarted, you can run the below command to find the Service Pack level of the SQL Server Instance that you have applied Service Pack..
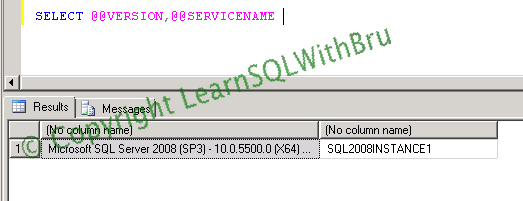
SELECT @@VERSION,@@SERVICENAME
You can see that the result shows (SP3).
Do you like this site? Like our FB page @ Facebook.com\LearnSQLWithBru so that, you know when there is a new blog post.
— Bru Medishetty