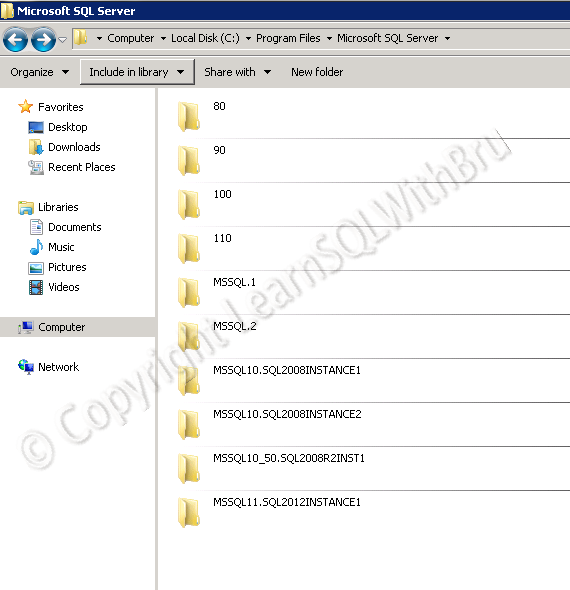
In this blog we shall take a look at the naming convention of SQL Server Instance directories since SQL Server 2005. By default, SQL Server is installed in C:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server directory. The Instance directory is then created depending on the SQL Server Version that is installed. For each SQL Instance installed, there would be a separate directory for that Instance, all the binary files of that instance are stored in that directory.
In SQL Server 2005, the instance directories are named as MSSQL.1, MSSQL.2, MSSQL.3 and so on as new Instances are installed. This is inconvenience to find the instances by looking at the naming of these directories. See below that there are 2 directories MSSQL.1and MSSQL.2 one of them being a default instance and the other one is obviously a named instance.
Where as starting from SQL Server 2008, the naming of the directories has been changed to reflect the Instance they belong to. Instance directory names in SQL 2008 start with MSSQL10. followed by the instance name. See that there are 2 directories named MSSQL10.SQL2008INSTANCE1 and MSSQL10.SQL2008INSTANCE2.
This naming convention has continued in the next releases of SQL Server, such as SQL 2008 R2 (which is often referred as 10.5) hence the naming is MSSQL10_5.xyz and finally in SQL Server 2012, the Instance directory is named as MSSQL11.xyz…
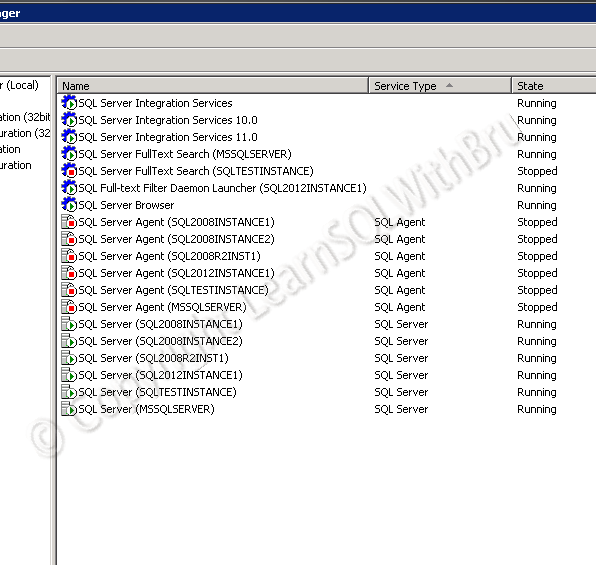
Finally this is how the SQL Server configuration Manager looks like on the server. There are total of 6 SQL Server Instances as you can see.
Do you like this site? Like our FB page @ Facebook.com\LearnSQLWithBru so that, you know when there is a new blog post.
— Bru Medishetty