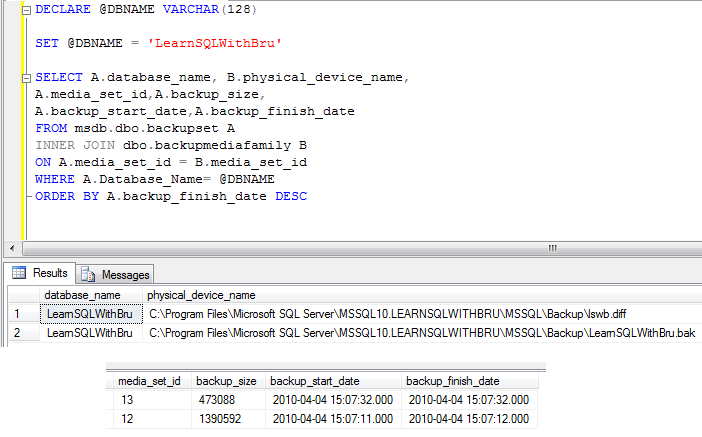
Few days back, I was asked this question. Using T-SQL is there a way to find the backup details about a database? Including physical location of the database where the backup of a particular database was performed. I did recollect that I wrote such a T-SQL query sometime back to find the backup locations of database backup. I came up with the below query that helped finds the backup information of a particular database.
Find the T- SQL Script at the end of the post. Remember to change the value of the local variable @DBNAME when running in your system. The query has been tested in SQL Server 2008.
The output of the query was wide enough not to fit in the image, hence it has been broken into 2 and displayed. The query displays the details in the reverse chronology, i.e the most recent backup first.
T-SQL Query used in the article
DECLARE @DBNAME VARCHAR(128) SET @DBNAME = 'DATABASENAME' SELECT A.database_name, B.physical_device_name ,A.media_set_id,A.backup_size, A.backup_start_date,A.backup_finish_date FROM msdb.dbo.backupset A INNER JOIN msdb.dbo.backupmediafamily B ON A.media_set_id = B.media_set_id WHERE A.Database_Name= @DBNAME ORDER BY A.backup_finish_date DESC
Do you like this site? Like our FB page @ Facebook.com\LearnSQLWithBru so that, you know when there is a new blog post.
— Bru Medishetty