This is one of the most frequently asked questions by people who are new to SQL Server. Since they are new to SQL Server, their concern is understandable. I was personally asked this question or this list multiple times and most recently, as comments to one of my blogs.
So I decided to list down a list of tasks and responsibilities carried out by a SQL Server DBA. Before further reading, let me tell you that roles and responsibilities of a SQL Server DBA varies from one organization to another as no two organizations IT setup are exactly similar. For better understanding, the text in the parenthesis (Italicized blue font) is the subject area or chapter that has the topics to carryout the responsibilities…
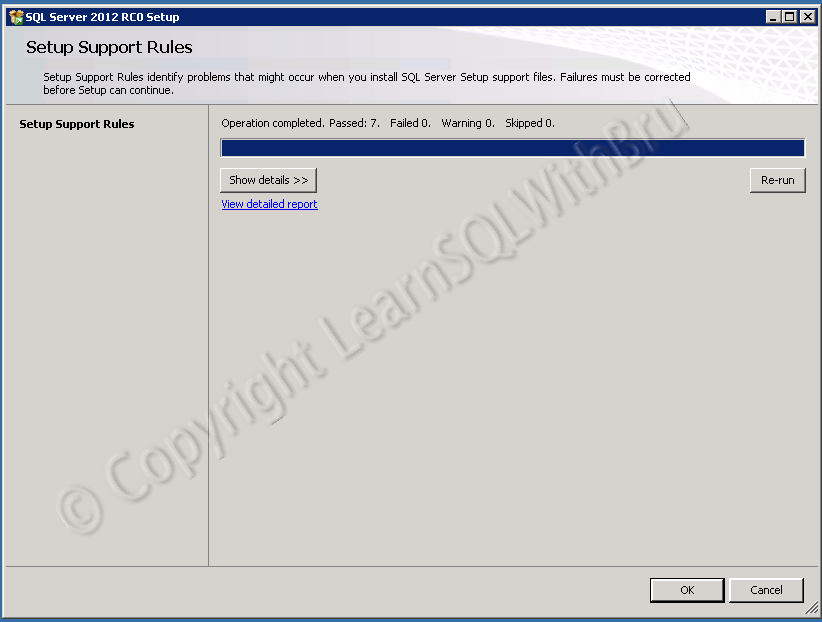
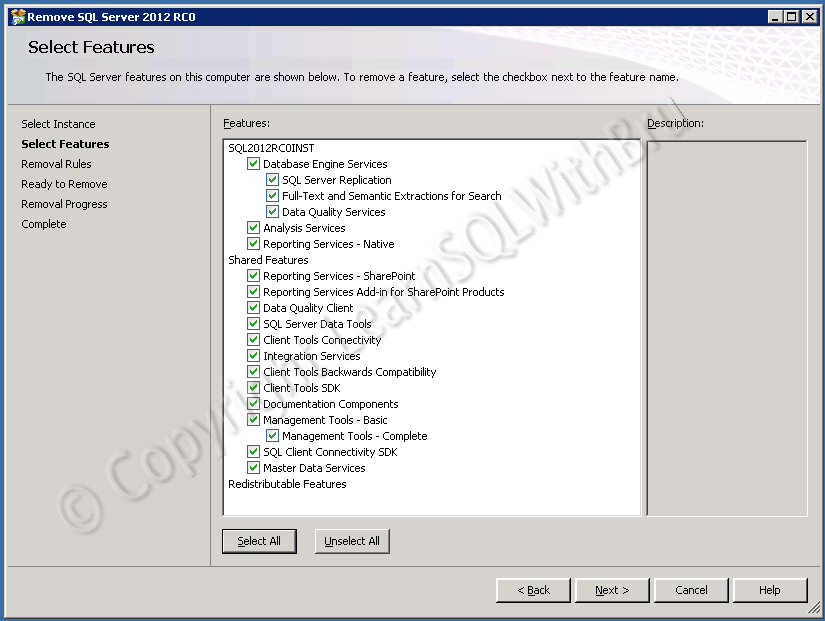
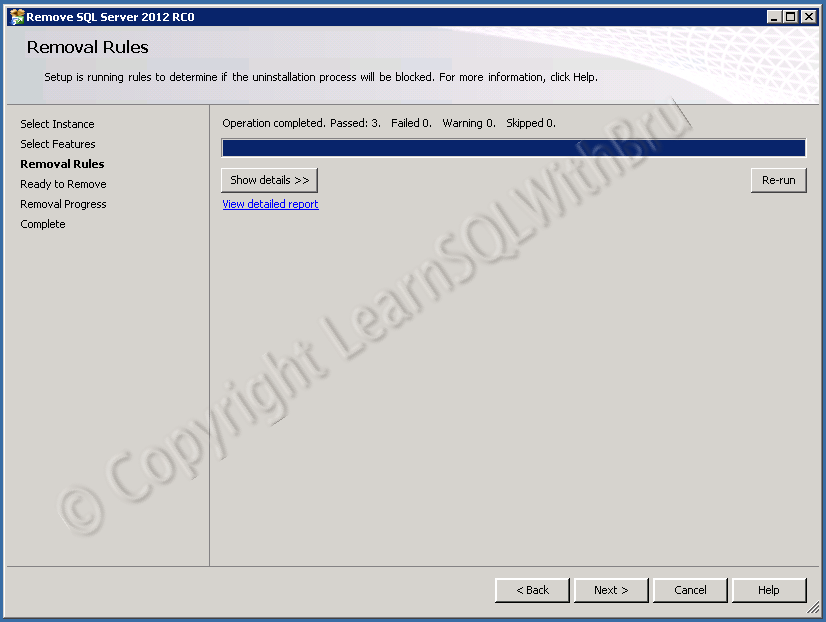
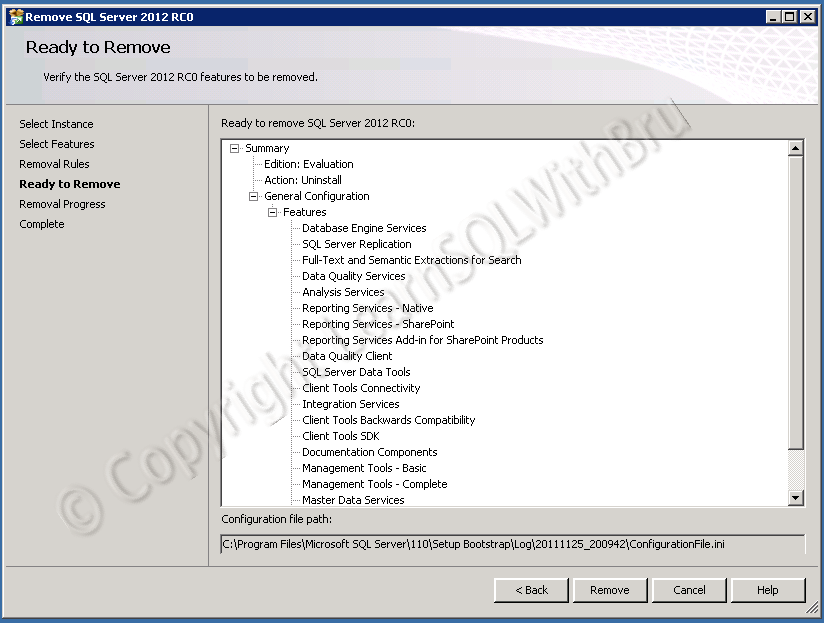
- Installation, Administration and Maintenance of SQL Server Instances. (Installing SQL Server)
- Setup Test, Dev, Staging and Production Environments. (Installing SQL Server)
- Create Users and assign permissions based on the level of database access the user would need. (Security)
- Create Linked Servers to SQL Servers and other databases such as Oracle, Access, Informix etc. (Security and General Administration)
- Design database Backup and Restoration Strategy. (Database Backups and SQL Server Agent)
- Once created the database Backups, monitor those backups are being performed regularly. (SQL Server Agent)
- From time to time recover the databases to a specific point of time, as per the requests. (Database Backups and Recovery)
- Setup High-Availability as part Disaster Recovery Strategy for the Databases. (Failover Clustering, Database Mirroring, Log Shipping and Replication)
- Troubleshoot various problems that arise in a day-to-day work and fix the issues. (Monitoring SQL Server Error Logs and checking your email alert (if there is one configured))
- Monitoring and Performance Tuning; Physical Server Level, Database level (Database settings and options) and query tuning. (Creating and maintaining those Indexes, not performing database shrinking, memory settings, monitoring CPU usage and Disk I/O activity etc)
- Documenting major changes to the SQL Servers. (General)
- Apply Service Packs. (General)
Note: These are only some of the roles carried out by a SQL Server DBA. If you have more questions, please let me know through comments..
Do you like this site? Like our FB page @ Facebook.com\LearnSQLWithBru so that, you know when there is a new blog post.
— Bru Medishetty