This blog is Part-II of last week’s blog post Create Linked Server to connect to a SQL Server Part – I. In this blog we shall learn two more ways of creating a Linked Server for a SQL Server destination.
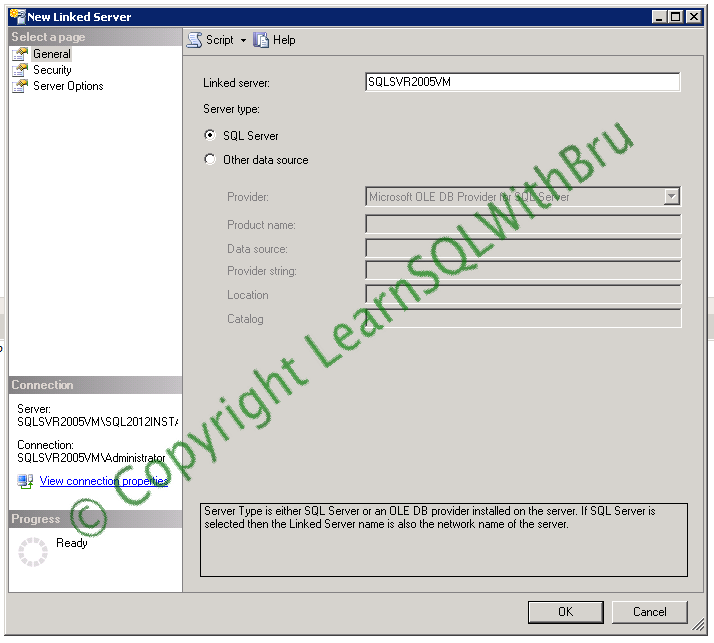
In the first part, we saw how to create a Linked Server using graphical interface from SSMS. In that method, we created linked server by selecting Other data source as Server type. In this method of creating Linked Server, we shall choose SQL Server as Server type and know more details about what is the difference when creating this way.
When creating Linked Server in this way, keep in mind that Linked Server name we are going to enter in the text box should be the same as the target SQL Server. If the target SQL instance is a named instance, you should be entering the full instance name as Servername\Instancename.
Security and Server Options in this method is same as as we saw in the first part of this blog, so I am avoiding explanation of those steps in this blog. Once you are done, choose OK to create the Linked Server.
Using T-SQL
You can also create a Linked Server using system stored procedure sp_addlinkedserver. Below screen shot shows the script that I used to create a linked server using the system stored procedure sp_addlinkedserver.
Do you like this site? Like our FB page @ Facebook.com\LearnSQLWithBru so that, you know when there is a new blog post.
–Bru Medishetty