This blog post is in response to a question / comment that to my blog posted earlier this week, if you haven’t read it, read it here Rules to follow while naming a SQL Server. I thought it would make sense when explained with examples instead of a short reply to that comment.
As with many things in IT, the simplest answer is “it depends”. So these examples that I am giving below are purely fictitious…
What to consider when naming the SQL Instance?
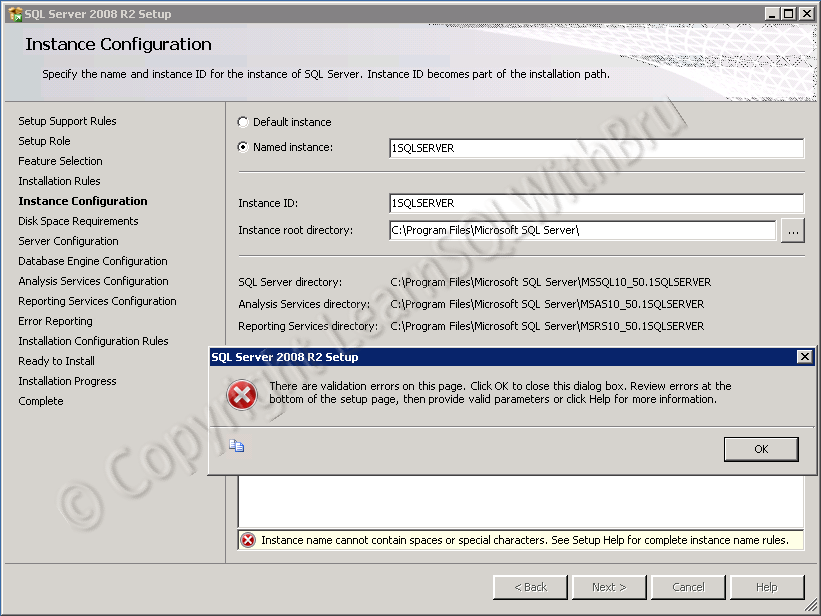
When naming a SQL Server Instance, I would consider the primary application that is going to use this SQL Server Instance, the location of the SQL Server and Environment the SQL Instance belongs to..
Let’s assume there is a Sales application and a SQL Server Instance in required for that application. The SQL Servers (QA, Dev and Prod) are going to be deployed in New York, I would name the SQL Server Instances as SLSNYCQAS, SLSNYCDEV and SLSNYCPRD.
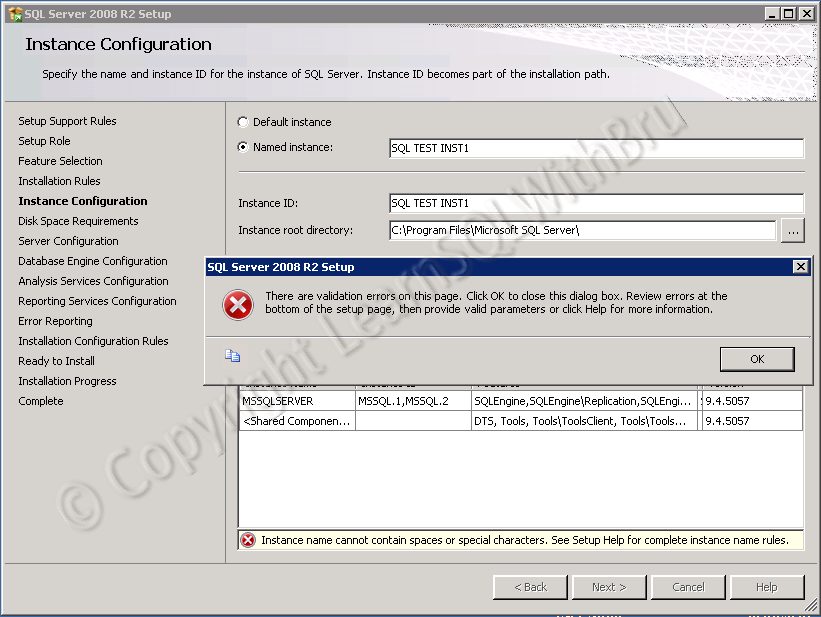
Another example where an organization named WhiteSun needs a SQL Instance for their Research & Development application, the SQL Instance names that I can think would be WSRNDSTG, WSRNDTRG, WSRNDTST, WSRNDDEV and WSRNDPRD. STG short code for Staging, TRG for Training, TST for Test etc.
There is no hard and fast rule that the Instance names should be ending with PRD, DEV and so on. These SQL Instance names mentioned above can be jumbled to make new names such as DEVSLSNYC or WSTSTRND as per the choice of the decision maker, be it a SQL Server DBA or a Project Manager..
Do you like this site? Like our FB page @ Facebook.com\LearnSQLWithBru so that, you know when there is a new blog post.
— Bru Medishetty