Few weeks back, I wrote a blog on CONCAT string function in SQL Server 2012. A user asked if the CONCAT function is similar to Space function in SQL Server and what is the difference between the two functions. I replied to him and clarified the difference of the 2 functions. After that I thought, it would be good to write a blog post on Space function too.
Space function
Space function is useful to return ‘x’ number of spaces, where ‘x’ is an integer. The syntax for the space function is space(x) where x is an integer. To understand the function lets us look a simple script with and without space function.
Without Space function
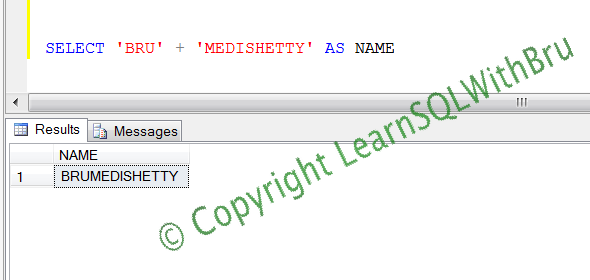
The below screen shot displays an output where 2 string values are concatenated without using space function and the resulting string is an output that may not be acceptable. See that the resulting string is a single string without any break between first and last name.
Using Space function
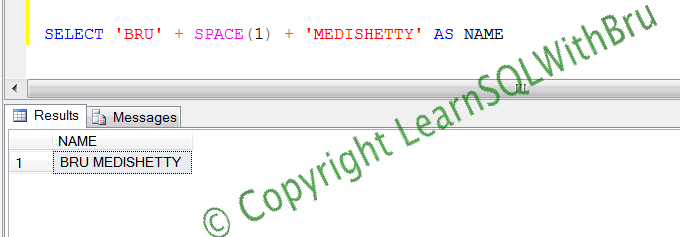
The below screen shot displays an output where 2 string values are concatenated and separated by space function. Using space(1) generated a single space (1 space) and when that is used in the string concatenation, output string is now better and acceptable.
Do you like this site? Like our FB page @ Facebook.com\LearnSQLWithBru to know when there is new content.
— Bru Medishetty